Yukon’s Electric Reliability Framework
 A product of the Energy Mines Ministers’ Conference
A product of the Energy Mines Ministers’ Conference
| Installed CapacityFootnote 1 | 148.1 MW |
| Annual GenerationFootnote 2 | 417 GWh |
| Annual Consumption | NA |
| Customers | ~ 21,000 |
| Annual Exports | 0 GWh |
| Annual Imports | 0 GWh |
| Transmission System length (≥66 kV) | ~ 957 km |
| Interconnections | none |
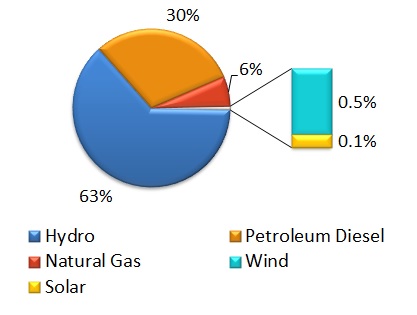
Installed Capacity Mix (2014)Footnote 3
Text version of Pie Chart
Pie Chart showing Yukon’s installed capacity mix (2014): hydro 63%, petroleum diesel 30%, natural gas 6%, and others less than 1%
The transmission and distribution of electricity in Yukon occurs over 6 isolated grids. The Energy Strategy for Yukon supports a shift towards cleaner, renewable sources of energy for the territory
Key Organizations
The Government of Yukon (YG) provides strategic direction, policy and monitoring services to Yukon’s electricity sector. YG is also responsible for the bulk of energy efficiency programs in the territory.
The Yukon Utilities Board (YUB) is a Regulatory Board that consists of three to five members, one of which is the Chair and one of which is the Vice-Chair. Members are appointed by the Government of Yukon.
The Yukon Development Corporation (YDC) is a Crown corporation of the Government of Yukon and the parent company to the Yukon Energy Corporation. YDC is currently acting as Yukon large energy infrastructure planner, and is evaluating the feasibility and financing of the Stewart/Keno Transmission Line and Yukon’s Next Generation Hydro Project.
The Yukon Energy Corporation (YEC) is a Crown corporation that operates as a utility, at arms-length from the Yukon government. YEC is the main generator and transmitter of electrical energy in Yukon.
ATCO Electric Yukon is a privately owned company of the ATCO Corporation in Alberta. It is a recognized distributer of electricity in the territory; purchasing power from Yukon Energy Corporation for distribution to its customers. ATCO is also a limited generator of electricity, owning 1.3MW installed hydro capacity, and 14.6MW of installed diesel capacity. ATCO is responsible for providing electricity to Yukon’s four remote communities.
Electric Reliability Framework in Yukon
Yukon’s transmission and distribution system is made up of six isolated power grids: the bulk of Yukon’s electricity is generated for and distributed to the Yukon Integrated System, while the remaining five systems - Old Crow community diesel, Beaver Creek community diesel, Burwash Landing/Destruction Bay community diesel, Swift River community diesel, and Watson Lake community diesel - service smaller areas. All systems are independent of the North American Bulk Electric System.
Yukon’s utilities are regulated by the Yukon Utilities Board (YUB). The YUB’s mandate, in summary, includes:
- issuing orders fixing rates of a public utility;
- prohibiting or limiting any proposed rate change;
- fixing proper and adequate rates and methods of depreciation, amortization or depletion in respect of the property of any public utility;
- fixing standards, classifications, regulations, practices, measurements or services to be observed, provided or followed by a public utility, and
- determining areas that services of a public utility shall provide.
Under the Yukon Public Utilities Act it is the responsibility the Yukon Utilities Board to regulate franchised utilities that generate, transmit and distribute power in the territory. Yukon currently (2016) has two franchised utilities, the publically-owned crown corporation Yukon Energy Corporation, and the privately-owned ATCO Electric Yukon. Both utilities are required to maintain sufficient spinning reserve to compensate for the loss of the largest generating unit during the system peak. This means that any of Yukon’s isolated grids can have more twice the generating capacity installed than what is required to meet peak winter load to ensure reliability. In practice, approximately 95 per cent of electricity generated in Yukon annually is produced from renewable resources such as hydro.
Yukon’s energy planning is comprised of three main documents:
- The Energy Strategy for Yukon;
- The 2016 Integrated Resource Plan (in process); and
- The Next Generation Hydro Project (in process).
See the top of the page for links to a province or territory.
Page details
- Date modified: