Tables for Calculating Effective Thermal Resistance of Opaque Assemblies
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- 1.0 Purpose
- 2.0 Methodology
- 3.0 Instructions
- 4.0 List of Tables
- 5.0 Thermal Resistance Tables
- Appendix A: Examples
1.0 Purpose
This document provides thermal resistance properties of opaque assembly materials required to calculate the total effective thermal resistance of building assemblies under the 2012 ENERGY STAR® for New Homes (ESNH) Standard. The format is designed to provide simple, easy-to-use look-up tables for the effective thermal resistance of portions of assemblies containing both framing members and cavity insulation, as well as continuous material layers (including air films).
Instructions are provided in Section 3.0 on how to use the tables. For most assemblies, the tables are organized as follows: (i) type of assembly (e.g. walls above grade), (ii) type of framing (e.g. dimensional lumber), (iii) framing member size (e.g. 2”x6”), and lastly, within each table (iv) framing on-centre spacing (e.g. 16”). A listing of tables that contains hyperlinks to each table is found on page 5. Appendix A provides examples of the calculation methodology for a variety of assembly types.
All comments and inquiries regarding this document should be addressed to:
New Housing
Housing Division
Office of Energy Efficiency
Natural Resources Canada
930 Carling Ave., Building #1
Ottawa, ON, K1Y 4X2
e-mail: NewHousingInquiries_nh@NRCan.gc.ca
2.0 Methodology
Overview
The tables and the methodology provided in this document allow users to calculate the total effective thermal resistance of common assemblies using the Isothermal Planes (Series-Parallel) method as described in 2009 ASHRAE Handbook—FundamentalsFootnote 1. The Isothermal Planes method is also proposed for the National Building Code of Canada (2012 revision) as the method for calculating the effective thermal resistance of opaque assemblies to demonstrate compliance with the minimum requirements of the code.
In wood frame construction the Isothermal Planes (Series-Parallel) method breaks the components in an assembly into two types: (i) a component which has parallel paths of heat flow, and (ii) continuous layers of homogeneous materials which are included in series. The component in which parallel heat flow occurs are assemblies containing both framing members and another material within the cavity, typically an insulation material – the frame-cavity component. Continuous layers in series are materials that overlay the frame-cavity component such as sheathing and gypsum board.
The Isothermal Planes (Series-Parallel) calculation can be described as:
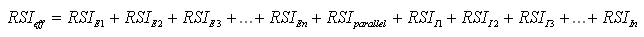
Text version
Isothermal Planes (Series-Parallel) calculation
This is a mathematical equation calculating the total effective thermal resistance of the assembly: calculated as RSI sub eff. The RSI sub eff is equal to the sum of continuous layers to the exterior of the frame-cavity component, the effective thermal resistance of the frame cavity component and continuous layers to the interior of the frame-cavity component. The RSI sub eff equals RSI sub E1 plus RSI sub E2 plus RSI sub E3 through RSI sub En, where RSI sub E are continuous layers to the exterior of the frame-cavity component, plus RSI sub parallel, where RSI sub parallel is the effective thermal resistance of the frame-cavity component, plus RSI sub I1 plus RSI sub I2 plus RSI sub I3 through RSI sub In, where RSI sub I are continuous layers to the interior of the frame-cavity component.
Where:
RSIeff is the total effective thermal resistance of the assembly,
RSIE are continuous layers to the exterior of the frame-cavity component,
RSIparallel is the effective thermal resistance of the frame-cavity component (Note: no continuous layers are included here, see ‘RSIparallel Tables’ below for more information), and
RSII are continuous layers to the interior of the frame-cavity component.
Equation 1 above can be simplified by summing all the continuous layers into one term, RSIseries to arrive at:
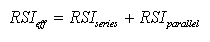
Text version
Simplified version of equation 1
This is a mathematical equation derived from equation 1. All of the continuous layers (RSI sub E1, RSI sub E2, RSI sub I1, RSI sub I2) have been summed into one term; RSI sub series. The simplified RSI sub eff is equal to the sum of RSI sub series and RSI sub parallel.
Values for RSIparallel can be obtained from the appropriate table for the assembly in Section 5.1, ‘Frame-Cavity Component’. Values for RSIseries can be calculated from the table of continuous material layers in Section 5.2 ‘Thermal Resistance of Continuous Materials’.
RSIparallel Tables
The RSIparallel tables provide the effective thermal resistance of the frame-cavity component of assemblies (the part which contains both framing members and cavity insulation, denoted in this document as RSIparallel).The effective thermal resistance values provided in the tables take into account the effect of thermal bridging of the framing members, and the resulting parallel heat flow paths through the framing and cavity insulation.
The tables provide the effective thermal resistance of the frame-cavity component over a wide range of nominal insulation values, in increments of approximately RSI 0.18 (R 1). The rationale for providing the wide range is allow for a variety of cavity insulation products, including batt, spray-applied and loose-fill insulation products.
The calculation method used is the parallel heat flow portion of the Isothermal Planes method as described in ASHRAE Fundamentals 2009. No continuous layers are included in the calculation of the effective thermal resistance in these tables. The parallel heat flow portion calculation is as follows:
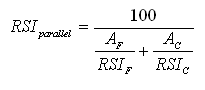
Text version
Parallel heat flow portion calculation
This is a mathematical equation calculating the parallel heat flow portion: calculated as RSI sub parallel. The RSI sub parallel is equal to 100 divided by the sum of A sub F, where A sub F is the percentage area of the assembly that the framing occupies, divided by RSI sub F, where RSI sub F is the thermal resistance of the framing number, and A sub C, where A sub C is the percentage area of the assembly that the cavity insulation occupies, divided by RSI sub C, where RSI sub C is the nominal thermal resistance of the cavity insulation component.
Where:
RSIparallel is the effective thermal resistance of the frame-cavity component,
AF is the percentage area of the assembly that the framing occupies,
RSIF is the thermal resistance of the framing member,
AC is the percentage area of the assembly that the cavity insulation occupies, and
RSIC is the nominal thermal resistance of the cavity insulation component.
The framing factor percentage areas (AF, AC) used in the calculation of these tables are those proposed for the 2010 National Building Code of Canada, Table A-9.36.2.4.(1).A. (2012 revision).
The thermal resistance of the framing members (RSIF) used in the tables is calculated by multiplying the per millimeter (mm) thermal resistance of the wood type by the depth of the member. For the wood type, these tables use the value 0.0085 (m2K/W)/mm as per the proposed National Building Code of Canada, Table A-9.36.2.4.(1).C. (2012 revision) for the species groups Spruce-Pine-Fir and Hem-Fir. The tables are eligible to be used for other wood-based framing materials with a thermal resistance greater than 0.0085 (m2K/W) /mm, such as framing members containing or composed of oriented strand board (OSB) and plywood, although the result may be conservative.
The tables are based on the assumption that the cavity insulation is a homogeneous material that completely fills the cavity.
3.0 Instructions
Use the following procedures to determine the total effective RSI value for the following assemblies:
- Roofs (Ceilings Below Attics, Cathedral Ceilings and Flat Roofs),
- Walls Above Grade (Walls Above and Not in Contact with the Ground),
- Foundation Walls (Walls Below and In Contact with the Ground),
- Floors Over Unheated Spaces,
- Unheated Floors on Ground,
- Heated Floors on Ground, and
- Slabs on Grade with Integral Footing.
Note that for assemblies consisting of only continuous layers such as (e) – (g), as well as assemblies using insulated concrete forms (ICFs), only Steps 2-4 below are required.
Steps:
1) Determine the thermal resistance of the cavity (RSIparallel)
Required information: assembly type, framing member type and size, on-centre spacing and cavity insulation nominal value.
- Go to Section 5.1 ‘Frame-Cavity Component’.
- Locate the table that matches your assembly in terms of the type and framing characteristics.
- In that table, read down the column of nominal thermal resistance to find your cavity insulation nominal value (provided in RSI and R value).
- Read across the row to find your on-centre spacing.
- Record the resultant effective thermal resistance value for the cavity component.
NOTES:
- The cavity insulation tables were developed on the assumption that the cavity insulation component is homogeneous and completely fills the frame cavity. There are some construction practices, such as in some cathedral ceilings, where the insulation does not completely fill the frame cavity in order to create a vented roof air space above the insulation. If no greater than a 50 mm roof air space is included above the insulation and between the framing members of a cathedral ceiling, the tables can be used in the normal manner, i.e., treat these assemblies as if the installed nominal insulation completely fills the cavity, and the vented air space is a continuous layer above the framing.
- If the nominal thermal resistance of the cavity insulation being used falls between two specified RSI/R values, the lower value must be applied (i.e., rounding up is not permitted).
- The Frame-Cavity Component tables indicate eligible surface air films or roof air spaces that may be included in the continuous layers of RSIseries (determined in Step 2). Additional layers, such as insulation, gypsum board and cladding, may also be added, where appropriate.2) Determine the thermal resistance of any continuous layers (RSIseries)
2) Required information: continuous layers in the assembly and location of eligible surface air films.
- Go to Table CM-1 ‘Continuous Materials’ in Section 5.2 ‘Thermal Resistance of Continuous Materials’.
- Locate your material, e.g., air film/space/cavity, cladding material, insulation material, and sheet materials.
- Read across the row to find the thermal resistance (in RSI) of your material.
- Determine the RSI value of your material:
- Where an ‘As listed’ RSI value is provided, record this value.
- Where a ‘Per mm’ RSI value is provided, a calculation to determine the effective RSI value is required. To do this, multiply the RSI/mm of the material by the thickness of the material (in millimeters (mm)), then round off this number to the nearest two decimal points (rounding up is permitted). Record this value.
- Repeat for all continuous layers in the assembly.
- Add the thermal resistance of all continuous layers in your assembly, including the eligible surface air films and the roof air space, if applicable.
NOTES:
- Where there is a continuous material that is exterior to a vented air space, it is excluded from calculation. This typically includes roof sheathing, and cladding installed on furring (e.g. rain screen construction).
- A polyethylene vapour retarder has a negligible contribution to effective thermal resistance and is therefore excluded from the calculation.
- The position of the interior face of the low-permeance insulating sheathing must be reviewed in terms of its thermal resistance relative to the overall thermal resistance of the wall, and the climate where the building is located, e.g., low-permeance requirements need to be considered for insulating sheathing installed on the exterior. For more information, refer to 9.25.5.2 of the National Building Code.
3) Determine RSIeff
Add RSIparallel determined in Step 1 and RSIseries determined in Step 2 to arrive at the total effective thermal resistance of the assembly of interest, denoted by RSIeff, per equation 1 in Section 2.0 Methodology above.
4) Check assembly for compliance with the minimum requirements
Compare RSIeff determined in Step 3 with the minimum requirement for the assembly.
The RSIeff must be equal to or greater than the total effective RSI value required in Table 2 of the 2012 ESNH Standard or the chosen level of insulation in the applicable Builder Option Package.
4.0 List of Tables
| ASSEMBLY | TABLE # | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roofs - Ceilings Below Attics, Cathedral Ceilings and Flat Roofs | Truss | Roof truss bottom chord dimensional lumber | 38 mm x 89 mm (2"x4") | R1-1 |
| 38 mm x 140 mm (2"x6") | R1-2 | |||
| Lumber Rafters and Joists | Dimensional lumber | 38 mm x 89 mm (2"x4") | R1-3 | |
| 38 mm x 140 mm (2"x6") | R1-4 | |||
| 38 mm x 184 mm (2"x8") | R1-5 | |||
| 38 mm x 235 mm (2"x10") | R1-6 | |||
| 38 mm x 286 mm (2"x12") | R1-7 | |||
| Roofs - Cathedral Ceilings and Flat Roofs | Engineered Wood I Joists and Trusses | 241 mm (9.5") depth | R2-1 | |
| 302 mm (11.875") depth | R2-2 | |||
| 356 mm (14") depth | R2-3 | |||
| Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs) | 1219 mm (48") on-centre | R2-4 | ||
| Roofs - Ceilings Below Attics | Raised Heel Truss | Roof truss bottom chord dimensional lumber | 38 mm x 89 mm (2"x4") | R3-1 |
| 38 mm x 140 mm (2"x6") | R3-2 | |||
| Walls Above and Not in Contact with Ground | Lumber Studs | Dimensional lumber | 38 mm x 89 mm (2"x4") | WA-1 |
| 38 mm x 140 mm (2"x6") | WA-2 | |||
| Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs) | 1219 mm (48") on-centre | WA-3 | ||
| Walls Below and in Contact with Ground | Lumber Studs | Dimensional lumber | 38 mm x 89 mm (2"x4") | WB-1 |
| 38 mm x 140 mm (2"x6") | WB-2 | |||
| Floors over Unheated Spaces | Lumber Joists | Floor joist dimensional lumber | 38 mm x 89 mm (2"x4") | FL-1 |
| 38 mm x 140 mm (2"x6") | FL-2 | |||
| 38 mm x 184 mm (2"x8") | FL-3 | |||
| 38 mm x 235 mm (2"x10") | FL-4 | |||
| 38 mm x 286 mm (2"x12") | FL-5 | |||
| Engineered Wood I Joists and Trusses | 241 mm (9.5") depth | FL-6 | ||
| 302 mm (11.875") depth | FL-7 | |||
| 356 mm (14") depth | FL-8 | |||
| Continuous Materials | CM-1 | |||
5.0 Thermal Resistance Tables
5.1 Frame-Cavity Component
Roofs - Ceilings Below Attics, Cathedral Ceilings and Flat Roofs
Table R1-1
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration3 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 1.59 | 9 | 1.36 | 1.38 | 1.40 | 1.42 |
| 1.76 | 10 | 1.46 | 1.48 | 1.51 | 1.54 |
| 1.94 | 11 | 1.56 | 1.59 | 1.62 | 1.66 |
| 2.11 | 12 | 1.65 | 1.69 | 1.72 | 1.76 |
| 2.29 | 13 | 1.74 | 1.78 | 1.83 | 1.87 |
| 2.46 | 14 | 1.82 | 1.87 | 1.92 | 1.97 |
| 2.64 | 15 | 1.90 | 1.96 | 2.01 | 2.07 |
| 2.82 | 16 | 1.98 | 2.04 | 2.10 | 2.17 |
| 2.99 | 17 | 2.05 | 2.12 | 2.18 | 2.26 |
| 3.17 | 18 | 2.12 | 2.19 | 2.27 | 2.35 |
| 3.34 | 19 | 2.18 | 2.26 | 2.34 | 2.43 |
| 3.52 | 20 | 2.25 | 2.33 | 2.42 | 2.51 |
| 3.70 | 21 | 2.31 | 2.40 | 2.49 | 2.59 |
NOTES:
- Applies to typical attic-type trusses and cathedral-type scissor trusses.
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Roof air space or exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior ceiling air film 0.11 m2K/W.
- Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 15.5% frame, 84.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 14% frame, 86% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 12.5% frame, 87.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 11% frame, 89% cavity.
Table R1-2
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration3 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 2.64 | 15 | 2.22 | 2.26 | 2.29 | 2.33 |
| 2.82 | 16 | 2.33 | 2.37 | 2.41 | 2.45 |
| 2.99 | 17 | 2.42 | 2.47 | 2.51 | 2.56 |
| 3.17 | 18 | 2.52 | 2.57 | 2.62 | 2.68 |
| 3.34 | 19 | 2.61 | 2.67 | 2.72 | 2.79 |
| 3.52 | 20 | 2.70 | 2.76 | 2.83 | 2.90 |
| 3.70 | 21 | 2.79 | 2.86 | 2.93 | 3.00 |
| 3.87 | 22 | 2.87 | 2.94 | 3.02 | 3.10 |
| 4.05 | 23 | 2.95 | 3.03 | 3.11 | 3.20 |
| 4.23 | 24 | 3.03 | 3.12 | 3.21 | 3.30 |
| 4.40 | 25 | 3.10 | 3.19 | 3.29 | 3.39 |
| 4.58 | 26 | 3.18 | 3.27 | 3.38 | 3.49 |
| 4.76 | 27 | 3.25 | 3.35 | 3.46 | 3.58 |
| 4.93 | 28 | 3.32 | 3.42 | 3.54 | 3.66 |
| 5.11 | 29 | 3.38 | 3.50 | 3.62 | 3.75 |
| 5.28 | 30 | 3.44 | 3.56 | 3.69 | 3.83 |
| 5.46 | 31 | 3.51 | 3.63 | 3.77 | 3.91 |
| 5.64 | 32 | 3.57 | 3.70 | 3.84 | 4.00 |
| 5.81 | 33 | 3.63 | 3.76 | 3.91 | 4.07 |
NOTES:
- Applies to typical attic-type trusses and cathedral-type scissor trusses.
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Roof air space or exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior ceiling air film 0.11 m2K/W.
- Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 15.5% frame, 84.5% cavity, 406 mm (16”): 14% frame, 86% cavity, 488mm (19.2”): 12.5% frame, 87.5% cavity, 610mm (24”): 11% frame, 89% cavity.
Table R1-3
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration2 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 1.59 | 9 | 1.37 | 1.39 | 1.41 | 1.43 |
| 1.76 | 10 | 1.48 | 1.50 | 1.53 | 1.55 |
| 1.94 | 11 | 1.58 | 1.61 | 1.64 | 1.68 |
| 2.11 | 12 | 1.68 | 1.71 | 1.75 | 1.79 |
| 2.29 | 13 | 1.77 | 1.81 | 1.86 | 1.90 |
| 2.46 | 14 | 1.85 | 1.90 | 1.95 | 2.01 |
| 2.64 | 15 | 1.94 | 1.99 | 2.05 | 2.11 |
| 2.82 | 16 | 2.02 | 2.08 | 2.15 | 2.22 |
| 2.99 | 17 | 2.09 | 2.16 | 2.23 | 2.31 |
| 3.17 | 18 | 2.17 | 2.24 | 2.32 | 2.40 |
| 3.34 | 19 | 2.23 | 2.31 | 2.40 | 2.49 |
| 3.52 | 20 | 2.30 | 2.39 | 2.48 | 2.58 |
| 3.70 | 21 | 2.37 | 2.46 | 2.56 | 2.66 |
NOTES:
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Roof air space or exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior ceiling air film 0.11 m2K/W.
- Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 14.5% frame, 85.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 13% frame, 87% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 11.5% frame, 88.5 cavity; 610 mm (24”): 10% frame, 90% cavity.
Table R1-4
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration2 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 2.64 | 15 | 2.24 | 2.28 | 2.32 | 2.35 |
| 2.82 | 16 | 2.35 | 2.39 | 2.44 | 2.48 |
| 2.99 | 17 | 2.45 | 2.50 | 2.55 | 2.60 |
| 3.17 | 18 | 2.55 | 2.61 | 2.66 | 2.72 |
| 3.34 | 19 | 2.65 | 2.70 | 2.77 | 2.83 |
| 3.52 | 20 | 2.74 | 2.81 | 2.87 | 2.94 |
| 3.70 | 21 | 2.83 | 2.90 | 2.98 | 3.06 |
| 3.87 | 22 | 2.92 | 2.99 | 3.07 | 3.16 |
| 4.05 | 23 | 3.00 | 3.09 | 3.17 | 3.27 |
| 4.23 | 24 | 3.09 | 3.18 | 3.27 | 3.37 |
| 4.40 | 25 | 3.16 | 3.26 | 3.36 | 3.47 |
| 4.58 | 26 | 3.24 | 3.34 | 3.45 | 3.56 |
| 4.76 | 27 | 3.32 | 3.42 | 3.54 | 3.66 |
| 4.93 | 28 | 3.39 | 3.50 | 3.62 | 3.75 |
| 5.11 | 29 | 3.46 | 3.58 | 3.71 | 3.84 |
| 5.28 | 30 | 3.52 | 3.65 | 3.78 | 3.93 |
| 5.46 | 31 | 3.59 | 3.72 | 3.87 | 4.02 |
| 5.64 | 32 | 3.66 | 3.80 | 3.94 | 4.10 |
| 5.81 | 33 | 3.72 | 3.86 | 4.02 | 4.19 |
NOTES:
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Roof air space or exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior ceiling air film 0.11 m2K/W.
- Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 14.5% frame, 85.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 13% frame, 87% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 11.5% frame, 85.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 10% frame, 90% cavity.
Table R1-5
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration2 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 3.34 | 19 | 2.87 | 2.91 | 2.95 | 3.00 |
| 3.52 | 20 | 2.98 | 3.03 | 3.08 | 3.13 |
| 3.70 | 21 | 3.09 | 3.14 | 3.20 | 3.26 |
| 3.87 | 22 | 3.19 | 3.25 | 3.31 | 3.37 |
| 4.05 | 23 | 3.29 | 3.36 | 3.42 | 3.49 |
| 4.23 | 24 | 3.39 | 3.46 | 3.54 | 3.61 |
| 4.40 | 25 | 3.48 | 3.56 | 3.64 | 3.72 |
| 4.58 | 26 | 3.58 | 3.66 | 3.75 | 3.84 |
| 4.76 | 27 | 3.67 | 3.76 | 3.85 | 3.95 |
| 4.93 | 28 | 3.76 | 3.85 | 3.95 | 4.06 |
| 5.11 | 29 | 3.85 | 3.95 | 4.05 | 4.17 |
| 5.28 | 30 | 3.93 | 4.03 | 4.15 | 4.27 |
| 5.46 | 31 | 4.01 | 4.12 | 4.24 | 4.37 |
| 5.64 | 32 | 4.09 | 4.21 | 4.34 | 4.47 |
| 5.81 | 33 | 4.17 | 4.29 | 4.43 | 4.57 |
| 5.99 | 34 | 4.25 | 4.38 | 4.52 | 4.67 |
| 6.16 | 35 | 4.32 | 4.46 | 4.60 | 4.76 |
| 6.34 | 36 | 4.39 | 4.54 | 4.69 | 4.86 |
| 6.52 | 37 | 4.47 | 4.62 | 4.78 | 4.95 |
| 6.69 | 38 | 4.53 | 4.69 | 4.86 | 5.04 |
| 6.87 | 39 | 4.60 | 4.77 | 4.94 | 5.13 |
| 7.04 | 40 | 4.67 | 4.84 | 5.02 | 5.21 |
| 7.22 | 41 | 4.74 | 4.91 | 5.10 | 5.30 |
| 7.40 | 42 | 4.80 | 4.98 | 5.18 | 5.39 |
| 7.57 | 43 | 4.86 | 5.05 | 5.25 | 5.47 |
NOTES:
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Roof air space or exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior ceiling air film 0.11 m2K/W.
- Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 14.5% frame, 85.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 13% frame, 87% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 11.5% frame, 88.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 10% frame, 90% cavity.
Table R1-6
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration2 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 4.40 | 25 | 3.75 | 3.81 | 3.87 | 3.93 |
| 4.58 | 26 | 3.86 | 3.92 | 3.99 | 4.06 |
| 4.76 | 27 | 3.96 | 4.03 | 4.11 | 4.18 |
| 4.93 | 28 | 4.06 | 4.14 | 4.22 | 4.30 |
| 5.11 | 29 | 4.17 | 4.25 | 4.33 | 4.42 |
| 5.28 | 30 | 4.26 | 4.35 | 4.44 | 4.53 |
| 5.46 | 31 | 4.36 | 4.46 | 4.55 | 4.65 |
| 5.64 | 32 | 4.46 | 4.56 | 4.66 | 4.77 |
| 5.81 | 33 | 4.55 | 4.65 | 4.76 | 4.88 |
| 5.99 | 34 | 4.64 | 4.75 | 4.87 | 4.99 |
| 6.16 | 35 | 4.73 | 4.85 | 4.97 | 5.10 |
| 6.34 | 36 | 4.82 | 4.94 | 5.07 | 5.21 |
| 6.52 | 37 | 4.91 | 5.04 | 5.17 | 5.32 |
| 6.69 | 38 | 4.99 | 5.12 | 5.27 | 5.42 |
| 6.87 | 39 | 5.07 | 5.22 | 5.37 | 5.52 |
| 7.04 | 40 | 5.15 | 5.30 | 5.46 | 5.62 |
| 7.40 | 42 | 5.32 | 5.47 | 5.64 | 5.82 |
| 7.57 | 43 | 5.39 | 5.56 | 5.73 | 5.92 |
| 7.75 | 44 | 5.47 | 5.64 | 5.82 | 6.02 |
| 7.93 | 45 | 5.54 | 5.72 | 5.91 | 6.11 |
| 8.10 | 46 | 5.61 | 5.80 | 5.99 | 6.20 |
| 8.28 | 47 | 5.69 | 5.88 | 6.08 | 6.30 |
| 8.45 | 48 | 5.75 | 5.95 | 6.16 | 6.39 |
| 8.63 | 49 | 5.83 | 6.03 | 6.25 | 6.48 |
| 8.81 | 50 | 5.89 | 6.10 | 6.33 | 6.57 |
| 8.98 | 51 | 5.96 | 6.17 | 6.41 | 6.65 |
| 9.16 | 52 | 6.03 | 6.25 | 6.49 | 6.74 |
| 9.33 | 53 | 6.09 | 6.32 | 6.56 | 6.82 |
| 9.51 | 54 | 6.15 | 6.39 | 6.64 | 6.91 |
| 9.69 | 55 | 6.22 | 6.46 | 6.72 | 7.00 |
NOTES:
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Roof air space or exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior ceiling air film 0.11 m2K/W.
- Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 14.5% frame, 85.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 13% frame, 87% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 11.5% frame, 88.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 10% frame, 90% cavity.
Table R1-7
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration2 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 5.28 | 30 | 4.51 | 4.58 | 4.65 | 4.73 |
| 5.46 | 31 | 4.62 | 4.70 | 4.78 | 4.86 |
| 5.64 | 32 | 4.73 | 4.81 | 4.90 | 4.98 |
| 5.81 | 33 | 4.84 | 4.92 | 5.01 | 5.10 |
| 5.99 | 34 | 4.94 | 5.03 | 5.13 | 5.23 |
| 6.16 | 35 | 5.04 | 5.14 | 5.24 | 5.34 |
| 6.34 | 36 | 5.14 | 5.24 | 5.35 | 5.46 |
| 6.52 | 37 | 5.24 | 5.35 | 5.46 | 5.58 |
| 6.69 | 38 | 5.33 | 5.45 | 5.57 | 5.69 |
| 6.87 | 39 | 5.43 | 5.55 | 5.68 | 5.81 |
| 7.04 | 40 | 5.52 | 5.65 | 5.78 | 5.92 |
| 7.22 | 41 | 5.62 | 5.75 | 5.89 | 6.03 |
| 7.40 | 42 | 5.71 | 5.85 | 5.99 | 6.14 |
| 7.57 | 43 | 5.79 | 5.94 | 6.09 | 6.25 |
| 7.75 | 44 | 5.88 | 6.03 | 6.19 | 6.36 |
| 7.93 | 45 | 5.97 | 6.13 | 6.29 | 6.47 |
| 8.10 | 46 | 6.05 | 6.22 | 6.39 | 6.57 |
| 8.28 | 47 | 6.14 | 6.31 | 6.49 | 6.67 |
| 8.45 | 48 | 6.22 | 6.39 | 6.58 | 6.77 |
| 8.63 | 49 | 6.30 | 6.48 | 6.67 | 6.88 |
| 8.81 | 50 | 6.38 | 6.57 | 6.77 | 6.98 |
| 9.16 | 52 | 6.54 | 6.74 | 6.95 | 7.17 |
| 9.51 | 54 | 6.69 | 6.90 | 7.12 | 7.37 |
| 9.86 | 56 | 6.83 | 7.06 | 7.30 | 7.55 |
| 10.21 | 58 | 6.97 | 7.21 | 7.46 | 7.73 |
| 10.57 | 60 | 7.12 | 7.36 | 7.63 | 7.92 |
NOTES:
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Roof air space or exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior ceiling air film 0.11 m2K/W.
- Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 14.5% frame, 85.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 13% frame, 87% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 11.5% frame, 88.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 10% frame, 90% cavity.
Roofs - Cathedral Ceilings and Flat Roofs
Table R2-1
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration4 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 4.40 | 25 | 3.93 | 3.99 | 4.05 | 4.12 |
| 4.58 | 26 | 4.05 | 4.12 | 4.19 | 4.26 |
| 4.76 | 27 | 4.18 | 4.25 | 4.33 | 4.41 |
| 4.93 | 28 | 4.30 | 4.38 | 4.46 | 4.55 |
| 5.11 | 29 | 4.42 | 4.50 | 4.59 | 4.69 |
| 5.28 | 30 | 4.53 | 4.62 | 4.72 | 4.82 |
| 5.46 | 31 | 4.65 | 4.75 | 4.85 | 4.96 |
| 5.64 | 32 | 4.76 | 4.87 | 4.98 | 5.10 |
| 5.81 | 33 | 4.87 | 4.99 | 5.11 | 5.23 |
| 5.99 | 34 | 4.98 | 5.11 | 5.23 | 5.37 |
| 6.16 | 35 | 5.09 | 5.22 | 5.35 | 5.50 |
| 6.34 | 36 | 5.20 | 5.33 | 5.48 | 5.63 |
| 6.52 | 37 | 5.30 | 5.45 | 5.60 | 5.76 |
| 6.69 | 38 | 5.40 | 5.56 | 5.72 | 5.89 |
| 6.87 | 39 | 5.51 | 5.67 | 5.84 | 6.02 |
| 7.04 | 40 | 5.61 | 5.77 | 5.95 | 6.14 |
| 7.40 | 42 | 5.81 | 5.99 | 6.19 | 6.40 |
| 7.57 | 43 | 5.90 | 6.09 | 6.30 | 6.52 |
| 7.75 | 44 | 6.00 | 6.20 | 6.41 | 6.64 |
| 7.93 | 45 | 6.09 | 6.30 | 6.52 | 6.76 |
| 8.10 | 46 | 6.18 | 6.40 | 6.63 | 6.88 |
| 8.28 | 47 | 6.28 | 6.50 | 6.74 | 7.00 |
| 8.45 | 48 | 6.36 | 6.60 | 6.85 | 7.12 |
| 8.63 | 49 | 6.45 | 6.69 | 6.95 | 7.24 |
| 8.81 | 50 | 6.54 | 6.79 | 7.06 | 7.35 |
NOTES:
- Applies to parallel chord trusses.
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Roof air space or exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior ceiling air film 0.11 m2K/W.
- Based on species groups Spruce-Pine-Fir and Hem-Fir. Other wood-based framing materials with a thermal resistance greater than 0.0085 (m2K/W) /mm, such as framing members containing or composed of OSB and plywood are also eligible.
- Equivalent Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 10.5% frame, 89.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 9% frame, 91% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 7.5% frame, 92.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 6% frame, 94% cavity.
Table R2-2
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration4 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 4.93 | 28 | 4.50 | 4.55 | 4.61 | 4.67 |
| 5.11 | 29 | 4.63 | 4.69 | 4.76 | 4.82 |
| 5.28 | 30 | 4.75 | 4.82 | 4.89 | 4.97 |
| 5.46 | 31 | 4.88 | 4.96 | 5.03 | 5.11 |
| 5.64 | 32 | 5.01 | 5.09 | 5.18 | 5.26 |
| 5.81 | 33 | 5.13 | 5.22 | 5.31 | 5.40 |
| 5.99 | 34 | 5.25 | 5.35 | 5.45 | 5.55 |
| 6.16 | 35 | 5.37 | 5.47 | 5.57 | 5.68 |
| 6.34 | 36 | 5.49 | 5.60 | 5.71 | 5.83 |
| 6.52 | 37 | 5.61 | 5.73 | 5.84 | 5.97 |
| 6.69 | 38 | 5.72 | 5.85 | 5.97 | 6.10 |
| 6.87 | 39 | 5.84 | 5.97 | 6.10 | 6.24 |
| 7.04 | 40 | 5.95 | 6.09 | 6.23 | 6.37 |
| 7.22 | 41 | 6.07 | 6.21 | 6.36 | 6.51 |
| 7.40 | 42 | 6.18 | 6.33 | 6.48 | 6.65 |
| 7.57 | 43 | 6.28 | 6.44 | 6.60 | 6.78 |
| 7.75 | 44 | 6.39 | 6.56 | 6.73 | 6.91 |
| 7.93 | 45 | 6.50 | 6.67 | 6.86 | 7.05 |
| 8.10 | 46 | 6.61 | 6.78 | 6.97 | 7.17 |
| 8.28 | 47 | 6.71 | 6.90 | 7.10 | 7.30 |
| 8.45 | 48 | 6.81 | 7.01 | 7.21 | 7.43 |
| 8.63 | 49 | 6.92 | 7.12 | 7.33 | 7.56 |
| 8.81 | 50 | 7.02 | 7.23 | 7.45 | 7.69 |
NOTES:
- Applies to parallel chord trusses.
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Roof air space or exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior ceiling air film 0.11 m2K/W.
- Based on species groups Spruce-Pine-Fir and Hem-Fir. Other wood-based framing materials with a thermal resistance greater than 0.0085 (m2K/W) /mm, such as framing members containing or composed of OSB and plywood are also eligible.
- Equivalent Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 10.5% frame, 89.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 9% frame, 91% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 7.5% frame, 92.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 6% frame, 94% cavity.
Table R2-3
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration4 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 5.46 | 31 | 5.03 | 5.09 | 5.15 | 5.21 |
| 5.64 | 32 | 5.17 | 5.23 | 5.30 | 5.36 |
| 5.81 | 33 | 5.30 | 5.37 | 5.43 | 5.51 |
| 5.99 | 34 | 5.43 | 5.50 | 5.58 | 5.66 |
| 6.16 | 35 | 5.56 | 5.63 | 5.72 | 5.80 |
| 6.34 | 36 | 5.69 | 5.77 | 5.86 | 5.95 |
| 6.52 | 37 | 5.81 | 5.91 | 6.00 | 6.10 |
| 6.69 | 38 | 5.94 | 6.03 | 6.13 | 6.24 |
| 6.87 | 39 | 6.06 | 6.17 | 6.27 | 6.38 |
| 7.04 | 40 | 6.18 | 6.29 | 6.40 | 6.52 |
| 7.22 | 41 | 6.30 | 6.42 | 6.54 | 6.67 |
| 7.40 | 42 | 6.42 | 6.55 | 6.68 | 6.81 |
| 7.57 | 43 | 6.54 | 6.67 | 6.80 | 6.94 |
| 7.75 | 44 | 6.66 | 6.80 | 6.94 | 7.09 |
| 7.93 | 45 | 6.78 | 6.92 | 7.07 | 7.23 |
| 8.10 | 46 | 6.89 | 7.04 | 7.20 | 7.36 |
| 8.28 | 47 | 7.00 | 7.16 | 7.33 | 7.50 |
| 8.45 | 48 | 7.11 | 7.28 | 7.45 | 7.63 |
| 8.63 | 49 | 7.23 | 7.40 | 7.58 | 7.77 |
| 8.81 | 50 | 7.34 | 7.52 | 7.71 | 7.90 |
| 8.98 | 51 | 7.44 | 7.63 | 7.83 | 8.03 |
| 9.16 | 52 | 7.55 | 7.75 | 7.95 | 8.17 |
| 9.33 | 53 | 7.66 | 7.86 | 8.07 | 8.29 |
NOTES:
- Applies to parallel chord trusses.
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Roof air space or exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior ceiling air film 0.11 m2K/W.
- Based on species groups Spruce-Pine-Fir and Hem-Fir. Other wood-based framing materials with a thermal resistance greater than 0.0085 (m2K/W) /mm, such as framing members containing or composed of OSB and plywood are also eligible.
- Equivalent Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 10.5% frame, 89.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 9% frame, 92.5% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 7.5% frame, 92.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 6% frame, 94% cavity.
Table R2-4
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Insulation Core/Framing Configuration (core depth & dimensional lumber size ) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 140 mm Insulation Core 38 mm x 140 mm (2"x6") frame with RSI=1.19 m2K/W |
184 mm Insulation Core 38 mm x 184 mm (2"x8") frame with RSI=1.56 m2K/W |
235 mm Insulation Core 38 mm x 235 mm (2"x10") frame with RSI=2.00 m2K/W |
|||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | |
| 3.35 | 19 | 2.88 | - | - | |
| 3.52 | 20 | 2.99 | - | - | |
| 3.70 | 21 | 3.11 | - | - | |
| 3.87 | 22 | 3.22 | - | - | |
| 4.05 | 23 | 3.33 | - | - | |
| 4.23 | 24 | 3.44 | - | - | |
| 4.40 | 25 | 3.54 | 3.78 | - | |
| 4.58 | 26 | 3.65 | 3.90 | - | |
| 4.76 | 27 | 3.75 | 4.02 | - | |
| 4.93 | 28 | 3.84 | 4.13 | - | |
| 5.11 | 29 | 3.94 | 4.24 | - | |
| 5.28 | 30 | 4.03 | 4.35 | - | |
| 5.46 | 31 | 4.13 | 4.46 | - | |
| 5.64 | 32 | 4.22 | 4.57 | - | |
| 5.81 | 33 | 4.31 | 4.67 | 4.96 | |
| 5.99 | 34 | 4.39 | 4.77 | 5.08 | |
| 6.16 | 35 | - | 4.87 | 5.19 | |
| 6.34 | 36 | - | 4.97 | 5.30 | |
| 6.52 | 37 | - | 5.07 | 5.42 | |
| 6.69 | 38 | - | 5.17 | 5.52 | |
| 6.87 | 39 | - | 5.26 | 5.63 | |
| 7.04 | 40 | - | 5.35 | 5.74 | |
| 7.22 | 41 | - | - | 5.84 | |
| 7.40 | 42 | - | - | 5.95 | |
| 7.57 | 43 | - | - | 6.05 | |
| 7.75 | 44 | - | - | 6.15 | |
| 7.93 | 45 | - | - | 6.26 | |
| 8.10 | 46 | - | - | 6.35 | |
| 8.28 | 47 | - | - | 6.45 | |
| 8.45 | 48 | - | - | 6.55 | |
NOTE:
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Roof air space or exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior ceiling air film 0.11 m2K/W.
Roofs - Ceilings Below Attics
Table R3-1
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance)4 |
Framing Configuration3 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 1.59 | 9 | 1.41 | 1.43 | 1.45 | 1.48 |
| 1.76 | 10 | 1.53 | 1.55 | 1.58 | 1.61 |
| 1.94 | 11 | 1.64 | 1.68 | 1.71 | 1.75 |
| 2.11 | 12 | 1.75 | 1.79 | 1.83 | 1.88 |
| 2.29 | 13 | 1.86 | 1.90 | 1.95 | 2.01 |
| 2.46 | 14 | 1.95 | 2.01 | 2.06 | 2.13 |
| 2.64 | 15 | 2.05 | 2.11 | 2.18 | 2.25 |
| 2.82 | 16 | 2.15 | 2.22 | 2.29 | 2.37 |
| 2.99 | 17 | 2.23 | 2.31 | 2.39 | 2.48 |
| 3.17 | 18 | 2.32 | 2.40 | 2.49 | 2.59 |
| 3.34 | 19 | 2.40 | 2.49 | 2.59 | 2.70 |
| 3.52 | 20 | 2.48 | 2.58 | 2.69 | 2.80 |
| 3.70 | 21 | 2.56 | 2.66 | 2.78 | 2.91 |
NOTES:
- Raised heel trusses eligible to use this table provide sufficient attic height at the eaves such that at least 80% of the depth of the installed insulation is achieved above the top plate of the exterior walls.
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Roof air space or exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior ceiling air film 0.11 m2K/W.
- Frame-Cavity – 304 mm (12”): 11.5% frame, 88.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 10% frame, 90% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 8.5% frame, 91.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 7% frame, 93% cavity.
- Denotes cavity only insulation for 38 mm x 89 mm (2"x4") construction. Remainder of insulation in ceilings below attic is met using continuous layers above the framing cavity. See Example 1 in Appendix A for an example using continuous layers and cavity insulation.
Table R3-2
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance)4 |
Framing Configuration3 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 2.64 | 15 | 2.32 | 2.35 | 2.39 | 2.43 |
| 2.82 | 16 | 2.44 | 2.48 | 2.53 | 2.57 |
| 2.99 | 17 | 2.55 | 2.60 | 2.65 | 2.70 |
| 3.17 | 18 | 2.66 | 2.72 | 2.78 | 2.84 |
| 3.34 | 19 | 2.77 | 2.83 | 2.90 | 2.97 |
| 3.52 | 20 | 2.87 | 2.94 | 3.02 | 3.10 |
| 3.70 | 21 | 2.98 | 3.06 | 3.14 | 3.22 |
| 3.87 | 22 | 3.07 | 3.16 | 3.25 | 3.34 |
| 4.05 | 23 | 3.17 | 3.27 | 3.36 | 3.47 |
| 4.23 | 24 | 3.27 | 3.37 | 3.48 | 3.59 |
| 4.40 | 25 | 3.36 | 3.47 | 3.58 | 3.70 |
| 4.58 | 26 | 3.45 | 3.56 | 3.69 | 3.82 |
| 4.76 | 27 | 3.54 | 3.66 | 3.79 | 3.93 |
| 4.93 | 28 | 3.62 | 3.75 | 3.89 | 4.04 |
| 5.11 | 29 | 3.71 | 3.84 | 3.99 | 4.15 |
| 5.28 | 30 | 3.78 | 3.93 | 4.09 | 4.26 |
| 5.46 | 31 | 3.87 | 4.02 | 4.18 | 4.36 |
| 5.64 | 32 | 3.94 | 4.10 | 4.28 | 4.47 |
| 5.81 | 33 | 4.02 | 4.19 | 4.37 | 4.57 |
NOTES:
- Raised heel trusses eligible to use this table provide sufficient attic height at the eaves such that at least 80% of the depth of the installed insulation is achieved above the top plate of the exterior walls.
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Roof air space or exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior ceiling air film 0.11 m2K/W.
- Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 11.5% frame, 88.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 10% frame, 90% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 8.5% frame, 91.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 7% frame, 93% cavity.
- Denotes cavity only insulation for 38 mm x 140 mm (2"x6") truss construction. Remainder of insulation in ceilings below attic is met using continuous layers above the framing cavity. See Example 1 in Appendix A for an example using continuous layers and cavity insulation.
Walls Above and Not in Contact with Ground
Table WA-1
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration2 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 1.59 | 9 | 1.25 | 1.27 | 1.29 | 1.30 |
| 1.76 | 10 | 1.33 | 1.35 | 1.37 | 1.39 |
| 1.94 | 11 | 1.40 | 1.43 | 1.45 | 1.48 |
| 2.11 | 12 | 1.47 | 1.49 | 1.52 | 1.55 |
| 2.29 | 13 | 1.53 | 1.56 | 1.59 | 1.63 |
| 2.46 | 14 | 1.59 | 1.62 | 1.66 | 1.70 |
| 2.64 | 15 | 1.64 | 1.68 | 1.72 | 1.76 |
| 2.82 | 16 | 1.69 | 1.73 | 1.78 | 1.82 |
| 2.99 | 17 | 1.74 | 1.78 | 1.83 | 1.88 |
| 3.17 | 18 | 1.78 | 1.83 | 1.88 | 1.94 |
| 3.34 | 19 | 1.82 | 1.87 | 1.93 | 1.98 |
| 3.52 | 20 | 1.86 | 1.91 | 1.97 | 2.03 |
| 3.70 | 21 | 1.89 | 1.95 | 2.01 | 2.08 |
NOTES:
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior wall air film 0.12 m2K/W.
- Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 24.5% frame, 75.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 23% frame, 77% cavity; 488 mm (19.2%): 21.5% frame, 78.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 20% frame, 80% cavity.
Table WA-2
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration2 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 2.99 | 17 | 2.18 | 2.22 | 2.26 | 2.30 |
| 3.17 | 18 | 2.25 | 2.29 | 2.33 | 2.38 |
| 3.34 | 19 | 2.32 | 2.36 | 2.41 | 2.45 |
| 3.52 | 20 | 2.38 | 2.43 | 2.48 | 2.53 |
| 3.70 | 21 | 2.44 | 2.49 | 2.55 | 2.60 |
| 3.87 | 22 | 2.49 | 2.55 | 2.61 | 2.67 |
| 4.05 | 23 | 2.55 | 2.61 | 2.67 | 2.74 |
| 4.23 | 24 | 2.60 | 2.66 | 2.73 | 2.80 |
| 4.40 | 25 | 2.65 | 2.72 | 2.78 | 2.86 |
| 4.58 | 26 | 2.70 | 2.77 | 2.84 | 2.92 |
| 4.76 | 27 | 2.74 | 2.82 | 2.89 | 2.98 |
| 4.93 | 28 | 2.79 | 2.86 | 2.94 | 3.03 |
| 5.11 | 29 | 2.83 | 2.91 | 2.99 | 3.08 |
| 5.28 | 30 | 2.87 | 2.95 | 3.04 | 3.13 |
| 5.46 | 31 | 2.91 | 2.99 | 3.08 | 3.18 |
| 5.64 | 32 | 2.94 | 3.03 | 3.13 | 3.23 |
| 5.81 | 33 | 2.98 | 3.07 | 3.17 | 3.27 |
NOTES:
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior wall air film 0.12 m2K/W.
- Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 24.5% frame, 75.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 23% frame, 77% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 21.5% frame, 78.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 20% frame, 80% cavity.
Table WA-3
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Insulation Core/Framing Configuration (core depth & dimensional lumber size ) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 89 mm Insulation Core 38 mm x 89 mm (2"x4") wood frame with RSI=0.757 m2K/W |
140 mm Insulation Core 38 mm x 140 mm (2"x6") wood frame with RSI=1.19 m2K/W |
184 mm Insulation Core 38 mm x 184 mm (2"x8") wood frame with RSI=1.56 m2K/W |
||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | ||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 2.11 | 12 | 1.69 | - | - |
| 2.29 | 13 | 1.78 | - | - |
| 2.47 | 14 | 1.88 | - | - |
| 2.64 | 15 | 1.96 | - | - |
| 2.82 | 16 | 2.04 | - | - |
| 2.99 | 17 | 2.12 | - | - |
| 3.17 | 18 | 2.19 | - | - |
| 3.35 | 19 | 2.26 | 2.67 | - |
| 3.52 | 20 | 2.33 | 2.76 | - |
| 3.70 | 21 | 2.40 | 2.86 | - |
| 3.87 | 22 | - | 2.94 | - |
| 4.05 | 23 | - | 3.03 | - |
| 4.23 | 24 | - | 3.12 | - |
| 4.40 | 25 | - | 3.19 | 3.51 |
| 4.58 | 26 | - | 3.27 | 3.61 |
| 4.76 | 27 | - | 3.35 | 3.70 |
| 4.93 | 28 | - | 3.42 | 3.79 |
| 5.11 | 29 | - | 3.50 | 3.88 |
| 5.28 | 30 | - | 3.56 | 3.96 |
| 5.46 | 31 | - | 3.63 | 4.05 |
| 5.64 | 32 | - | 3.70 | 4.13 |
| 5.81 | 33 | - | 3.76 | 4.21 |
| 5.99 | 34 | - | 3.83 | 4.29 |
| 6.16 | 35 | - | - | 4.36 |
| 6.34 | 36 | - | - | 4.44 |
| 6.52 | 37 | - | - | 4.52 |
| 6.69 | 38 | - | - | 4.59 |
| 6.87 | 39 | - | - | 4.66 |
| 7.04 | 40 | - | - | 4.72 |
NOTE:
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior wall air film 0.12 m2K/W.
Walls Below and in Contact with Ground
Table WB-1
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration2 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 1.59 | 9 | 1.33 | 1.35 | 1.37 | 1.39 |
| 1.76 | 10 | 1.43 | 1.45 | 1.48 | 1.50 |
| 1.94 | 11 | 1.52 | 1.55 | 1.58 | 1.61 |
| 2.11 | 12 | 1.61 | 1.64 | 1.68 | 1.71 |
| 2.29 | 13 | 1.69 | 1.73 | 1.77 | 1.81 |
| 2.46 | 14 | 1.76 | 1.81 | 1.85 | 1.90 |
| 2.64 | 15 | 1.84 | 1.89 | 1.94 | 1.99 |
| 2.82 | 16 | 1.91 | 1.96 | 2.02 | 2.08 |
| 2.99 | 17 | 1.97 | 2.03 | 2.09 | 2.16 |
| 3.17 | 18 | 2.03 | 2.10 | 2.17 | 2.24 |
| 3.34 | 19 | 2.09 | 2.16 | 2.23 | 2.31 |
| 3.52 | 20 | 2.15 | 2.22 | 2.30 | 2.39 |
| 3.70 | 21 | 2.20 | 2.28 | 2.37 | 2.46 |
NOTES:
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Interior wall air film 0.12 m2K/W.
- Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 17.5% frame, 82.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 16% frame, 84% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 14.5% frame, 85.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 13% frame, 87% cavity.
Table WB-2
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration2 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 2.99 | 17 | 2.36 | 2.41 | 2.45 | 2.50 |
| 3.17 | 18 | 2.46 | 2.50 | 2.55 | 2.61 |
| 3.34 | 19 | 2.54 | 2.59 | 2.65 | 2.70 |
| 3.52 | 20 | 2.62 | 2.68 | 2.74 | 2.81 |
| 3.70 | 21 | 2.70 | 2.77 | 2.83 | 2.90 |
| 3.87 | 22 | 2.78 | 2.84 | 2.92 | 2.99 |
| 4.05 | 23 | 2.85 | 2.93 | 3.00 | 3.09 |
| 4.23 | 24 | 2.92 | 3.00 | 3.09 | 3.18 |
| 4.40 | 25 | 2.99 | 3.07 | 3.16 | 3.26 |
| 4.58 | 26 | 3.06 | 3.15 | 3.24 | 3.34 |
| 4.76 | 27 | 3.12 | 3.22 | 3.32 | 3.42 |
| 4.93 | 28 | 3.18 | 3.28 | 3.39 | 3.50 |
| 5.11 | 29 | 3.24 | 3.35 | 3.46 | 3.58 |
| 5.28 | 30 | 3.30 | 3.41 | 3.52 | 3.65 |
| 5.46 | 31 | 3.35 | 3.47 | 3.59 | 3.72 |
| 5.64 | 32 | 3.41 | 3.53 | 3.66 | 3.80 |
| 5.81 | 33 | 3.46 | 3.58 | 3.72 | 3.86 |
NOTES:
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Interior wall air film 0.12 m2K/W.
- Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 17.5% frame, 82.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 16% frame, 84% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 14.5% frame, 85.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 13% frame, 87% cavity.
Floors over Unheated Spaces
Table FL-1
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration2 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 1.59 | 9 | 1.37 | 1.39 | 1.41 | 1.43 |
| 1.76 | 10 | 1.48 | 1.50 | 1.53 | 1.55 |
| 1.94 | 11 | 1.58 | 1.61 | 1.64 | 1.68 |
| 2.11 | 12 | 1.68 | 1.71 | 1.75 | 1.79 |
| 2.29 | 13 | 1.77 | 1.81 | 1.86 | 1.90 |
| 2.46 | 14 | 1.85 | 1.90 | 1.95 | 2.01 |
| 2.64 | 15 | 1.94 | 1.99 | 2.05 | 2.11 |
| 2.82 | 16 | 2.02 | 2.08 | 2.15 | 2.22 |
| 2.99 | 17 | 2.09 | 2.16 | 2.23 | 2.31 |
| 3.17 | 18 | 2.17 | 2.24 | 2.32 | 2.40 |
| 3.34 | 19 | 2.23 | 2.31 | 2.40 | 2.49 |
| 3.52 | 20 | 2.30 | 2.39 | 2.48 | 2.58 |
| 3.70 | 21 | 2.37 | 2.46 | 2.56 | 2.66 |
NOTES:
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior floor air film 0.16 m2K/W.
- Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 14.5% frame, 85.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 13% frame, 87% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 11.5% frame, 88.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 10% frame, 90% cavity.
Table FL-2
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration2 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 2.64 | 15 | 2.24 | 2.28 | 2.32 | 2.35 |
| 2.82 | 16 | 2.35 | 2.39 | 2.44 | 2.48 |
| 2.99 | 17 | 2.45 | 2.50 | 2.55 | 2.60 |
| 3.17 | 18 | 2.55 | 2.61 | 2.66 | 2.72 |
| 3.35 | 19 | 2.65 | 2.70 | 2.77 | 2.83 |
| 3.52 | 20 | 2.74 | 2.81 | 2.87 | 2.94 |
| 3.70 | 21 | 2.83 | 2.90 | 2.98 | 3.06 |
| 3.87 | 22 | 2.92 | 2.99 | 3.07 | 3.16 |
| 4.05 | 23 | 3.00 | 3.09 | 3.17 | 3.27 |
| 4.23 | 24 | 3.09 | 3.18 | 3.27 | 3.37 |
| 4.40 | 25 | 3.16 | 3.26 | 3.36 | 3.47 |
| 4.58 | 26 | 3.24 | 3.34 | 3.45 | 3.56 |
| 4.76 | 27 | 3.32 | 3.42 | 3.54 | 3.66 |
| 4.93 | 28 | 3.39 | 3.50 | 3.62 | 3.75 |
| 5.11 | 29 | 3.46 | 3.58 | 3.71 | 3.84 |
| 5.28 | 30 | 3.52 | 3.65 | 3.78 | 3.93 |
| 5.46 | 31 | 3.59 | 3.72 | 3.87 | 4.02 |
| 5.64 | 32 | 3.66 | 3.80 | 3.94 | 4.10 |
| 5.81 | 33 | 3.72 | 3.86 | 4.02 | 4.19 |
NOTES:
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior floor air film 0.16 m2K/W.
- Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 14.5% frame, 85.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 13% frame, 87% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 11.5% frame, 88.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 10% frame, 90% cavity.
Table FL-3
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration2 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 3.35 | 19 | 2.87 | 2.91 | 2.95 | 3.00 |
| 3.52 | 20 | 2.98 | 3.03 | 3.08 | 3.13 |
| 3.70 | 21 | 3.09 | 3.14 | 3.20 | 3.26 |
| 3.87 | 22 | 3.19 | 3.25 | 3.31 | 3.37 |
| 4.05 | 23 | 3.29 | 3.36 | 3.42 | 3.49 |
| 4.23 | 24 | 3.39 | 3.46 | 3.54 | 3.61 |
| 4.40 | 25 | 3.48 | 3.56 | 3.64 | 3.72 |
| 4.58 | 26 | 3.58 | 3.66 | 3.75 | 3.84 |
| 4.76 | 27 | 3.67 | 3.76 | 3.85 | 3.95 |
| 4.93 | 28 | 3.76 | 3.85 | 3.95 | 4.06 |
| 5.11 | 29 | 3.85 | 3.95 | 4.05 | 4.17 |
| 5.28 | 30 | 3.93 | 4.03 | 4.15 | 4.27 |
| 5.46 | 31 | 4.01 | 4.12 | 4.24 | 4.37 |
| 5.64 | 32 | 4.09 | 4.21 | 4.34 | 4.47 |
| 5.81 | 33 | 4.17 | 4.29 | 4.43 | 4.57 |
| 5.99 | 34 | 4.25 | 4.38 | 4.52 | 4.67 |
| 6.16 | 35 | 4.32 | 4.46 | 4.60 | 4.76 |
| 6.34 | 36 | 4.39 | 4.54 | 4.69 | 4.86 |
| 6.52 | 37 | 4.47 | 4.62 | 4.78 | 4.95 |
| 6.69 | 38 | 4.53 | 4.69 | 4.86 | 5.04 |
| 6.87 | 39 | 4.60 | 4.77 | 4.94 | 5.13 |
| 7.04 | 40 | 4.67 | 4.84 | 5.02 | 5.21 |
| 7.22 | 41 | 4.74 | 4.91 | 5.10 | 5.30 |
| 7.40 | 42 | 4.80 | 4.98 | 5.18 | 5.39 |
| 7.57 | 43 | 4.86 | 5.05 | 5.25 | 5.47 |
NOTES:
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior floor air film 0.16 m2K/W.
- Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 14.5% frame, 85.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 13% frame, 87% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 11.5% frame, 88.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 10% frame, 90% cavity.
Table FL-4
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration2 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 4.40 | 25 | 3.75 | 3.81 | 3.87 | 3.93 |
| 4.58 | 26 | 3.86 | 3.92 | 3.99 | 4.06 |
| 4.76 | 27 | 3.96 | 4.03 | 4.11 | 4.18 |
| 4.93 | 28 | 4.06 | 4.14 | 4.22 | 4.30 |
| 5.11 | 29 | 4.17 | 4.25 | 4.33 | 4.42 |
| 5.28 | 30 | 4.26 | 4.35 | 4.44 | 4.53 |
| 5.46 | 31 | 4.36 | 4.46 | 4.55 | 4.65 |
| 5.64 | 32 | 4.46 | 4.56 | 4.66 | 4.77 |
| 5.81 | 33 | 4.55 | 4.65 | 4.76 | 4.88 |
| 5.99 | 34 | 4.64 | 4.75 | 4.87 | 4.99 |
| 6.16 | 35 | 4.73 | 4.85 | 4.97 | 5.10 |
| 6.34 | 36 | 4.82 | 4.94 | 5.07 | 5.21 |
| 6.52 | 37 | 4.91 | 5.04 | 5.17 | 5.32 |
| 6.69 | 38 | 4.99 | 5.12 | 5.27 | 5.42 |
| 6.87 | 39 | 5.07 | 5.22 | 5.37 | 5.52 |
| 7.04 | 40 | 5.15 | 5.30 | 5.46 | 5.62 |
| 7.40 | 42 | 5.32 | 5.47 | 5.64 | 5.82 |
| 7.57 | 43 | 5.39 | 5.56 | 5.73 | 5.92 |
| 7.75 | 44 | 5.47 | 5.64 | 5.82 | 6.02 |
| 7.93 | 45 | 5.54 | 5.72 | 5.91 | 6.11 |
| 8.10 | 46 | 5.61 | 5.80 | 5.99 | 6.20 |
| 8.28 | 47 | 5.69 | 5.88 | 6.08 | 6.30 |
| 8.45 | 48 | 5.75 | 5.95 | 6.16 | 6.39 |
| 8.63 | 49 | 5.83 | 6.03 | 6.25 | 6.48 |
| 8.81 | 50 | 5.89 | 6.10 | 6.33 | 6.57 |
| 8.98 | 51 | 5.96 | 6.17 | 6.41 | 6.65 |
| 9.16 | 52 | 6.03 | 6.25 | 6.49 | 6.74 |
| 9.33 | 53 | 6.09 | 6.32 | 6.56 | 6.82 |
| 9.51 | 54 | 6.15 | 6.39 | 6.64 | 6.91 |
| 9.69 | 55 | 6.22 | 6.46 | 6.72 | 7.00 |
NOTES:
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior floor air film 0.16 m2K/W.
- Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 14.5% frame, 85.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 13% frame, 87% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 11.5% frame, 88.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 10% frame, 90% cavity.
Table FL-5
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration (frame-cavity percentage & on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 5.28 | 30 | 4.51 | 4.58 | 4.65 | 4.73 |
| 5.46 | 31 | 4.62 | 4.70 | 4.78 | 4.86 |
| 5.64 | 32 | 4.73 | 4.81 | 4.90 | 4.98 |
| 5.81 | 33 | 4.84 | 4.92 | 5.01 | 5.10 |
| 5.99 | 34 | 4.94 | 5.03 | 5.13 | 5.23 |
| 6.16 | 35 | 5.04 | 5.14 | 5.24 | 5.34 |
| 6.34 | 36 | 5.14 | 5.24 | 5.35 | 5.46 |
| 6.52 | 37 | 5.24 | 5.35 | 5.46 | 5.58 |
| 6.69 | 38 | 5.33 | 5.45 | 5.57 | 5.69 |
| 6.87 | 39 | 5.43 | 5.55 | 5.68 | 5.81 |
| 7.04 | 40 | 5.52 | 5.65 | 5.78 | 5.92 |
| 7.22 | 41 | 5.62 | 5.75 | 5.89 | 6.03 |
| 7.40 | 42 | 5.71 | 5.85 | 5.99 | 6.14 |
| 7.57 | 43 | 5.79 | 5.94 | 6.09 | 6.25 |
| 7.75 | 44 | 5.88 | 6.03 | 6.19 | 6.36 |
| 7.93 | 45 | 5.97 | 6.13 | 6.29 | 6.47 |
| 8.10 | 46 | 6.05 | 6.22 | 6.39 | 6.57 |
| 8.28 | 47 | 6.14 | 6.31 | 6.49 | 6.67 |
| 8.45 | 48 | 6.22 | 6.39 | 6.58 | 6.77 |
| 8.63 | 49 | 6.30 | 6.48 | 6.67 | 6.88 |
| 8.81 | 50 | 6.38 | 6.57 | 6.77 | 6.98 |
| 9.16 | 52 | 6.54 | 6.74 | 6.95 | 7.17 |
| 9.51 | 54 | 6.69 | 6.90 | 7.12 | 7.37 |
| 9.86 | 56 | 6.83 | 7.06 | 7.30 | 7.55 |
| 10.21 | 58 | 6.97 | 7.21 | 7.46 | 7.73 |
| 10.57 | 60 | 7.12 | 7.36 | 7.63 | 7.92 |
NOTES:
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior floor air film 0.16 m2K/W.
- Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 14.5% frame, 85.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 13% frame, 87% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 11.5% frame, 88.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 10% frame, 90% cavity.
Table FL-6
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration4 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 4.40 | 25 | 4.33 | 3.99 | 4.05 | 4.12 |
| 4.58 | 26 | 4.50 | 4.12 | 4.19 | 4.26 |
| 4.76 | 27 | 4.67 | 4.25 | 4.33 | 4.41 |
| 4.93 | 28 | 4.83 | 4.38 | 4.46 | 4.55 |
| 5.11 | 29 | 5.00 | 4.50 | 4.59 | 4.69 |
| 5.28 | 30 | 5.16 | 4.62 | 4.72 | 4.82 |
| 5.46 | 31 | 5.33 | 4.75 | 4.85 | 4.96 |
| 5.64 | 32 | 5.50 | 4.87 | 4.98 | 5.10 |
| 5.81 | 33 | 5.65 | 4.99 | 5.11 | 5.23 |
| 5.99 | 34 | 5.82 | 5.11 | 5.23 | 5.37 |
| 6.16 | 35 | 5.98 | 5.22 | 5.35 | 5.50 |
| 6.34 | 36 | 6.15 | 5.33 | 5.48 | 5.63 |
| 6.52 | 37 | 6.31 | 5.45 | 5.60 | 5.76 |
| 6.69 | 38 | 6.47 | 5.56 | 5.72 | 5.89 |
| 6.87 | 39 | 6.64 | 5.67 | 5.84 | 6.02 |
| 7.04 | 40 | 6.79 | 5.77 | 5.95 | 6.14 |
| 7.40 | 42 | 7.12 | 5.99 | 6.19 | 6.40 |
| 7.57 | 43 | 7.28 | 6.09 | 6.30 | 6.52 |
| 7.75 | 44 | 7.44 | 6.20 | 6.41 | 6.64 |
| 7.93 | 45 | 7.60 | 6.30 | 6.52 | 6.76 |
| 8.10 | 46 | 7.76 | 6.40 | 6.63 | 6.88 |
| 8.28 | 47 | 7.92 | 6.50 | 6.74 | 7.00 |
| 8.45 | 48 | 8.07 | 6.60 | 6.85 | 7.12 |
| 8.63 | 49 | 8.23 | 6.69 | 6.95 | 7.24 |
| 8.81 | 50 | 8.39 | 6.79 | 7.06 | 7.35 |
NOTES:
- Applies to parallel chord trusses.
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior floor air film 0.16 m2K/W.
- Based on species groups Spruce-Pine-Fir and Hem-Fir. Other wood-based framing materials with a thermal resistance greater than 0.0085 (m2K/W) /mm, such as framing members containing or composed of OSB and plywood are also eligible.
- Equivalent Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 10.5% frame, 89.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 9% frame, 91% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 7.5% frame, 92.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 6% frame, 94% cavity.
Table FL-7
| Cavity Insulation Component (Nominal Thermal Resistance) |
Framing Configuration4 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 4.93 | 28 | 4.50 | 4.55 | 4.61 | 4.67 |
| 5.11 | 29 | 4.63 | 4.69 | 4.76 | 4.82 |
| 5.28 | 30 | 4.75 | 4.82 | 4.89 | 4.97 |
| 5.46 | 31 | 4.88 | 4.96 | 5.03 | 5.11 |
| 5.64 | 32 | 5.01 | 5.09 | 5.18 | 5.26 |
| 5.81 | 33 | 5.13 | 5.22 | 5.31 | 5.40 |
| 5.99 | 34 | 5.25 | 5.35 | 5.45 | 5.55 |
| 6.16 | 35 | 5.37 | 5.47 | 5.57 | 5.68 |
| 6.34 | 36 | 5.49 | 5.60 | 5.71 | 5.83 |
| 6.52 | 37 | 5.61 | 5.73 | 5.84 | 5.97 |
| 6.69 | 38 | 5.72 | 5.85 | 5.97 | 6.10 |
| 6.87 | 39 | 5.84 | 5.97 | 6.10 | 6.24 |
| 7.04 | 40 | 5.95 | 6.09 | 6.23 | 6.37 |
| 7.22 | 41 | 6.07 | 6.21 | 6.36 | 6.51 |
| 7.40 | 42 | 6.18 | 6.33 | 6.48 | 6.65 |
| 7.57 | 43 | 6.28 | 6.44 | 6.60 | 6.78 |
| 7.75 | 44 | 6.39 | 6.56 | 6.73 | 6.91 |
| 7.93 | 45 | 6.50 | 6.67 | 6.86 | 7.05 |
| 8.10 | 46 | 6.61 | 6.78 | 6.97 | 7.17 |
| 8.28 | 47 | 6.71 | 6.90 | 7.10 | 7.30 |
| 8.45 | 48 | 6.81 | 7.01 | 7.21 | 7.43 |
| 8.63 | 49 | 6.92 | 7.12 | 7.33 | 7.56 |
| 8.81 | 50 | 7.02 | 7.23 | 7.45 | 7.69 |
NOTES:
- Applies to parallel chord trusses.
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior floor air film 0.16 m2K/W.
- Based on species groups Spruce-Pine-Fir and Hem-Fir. Other wood-based framing materials with a thermal resistance greater than 0.0085 (m2K/W) /mm, such as framing members containing or composed of OSB and plywood are also eligible.
- Equivalent Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 10.5% frame, 89.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 9% frame, 91% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 7.5% frame, 92.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 6% frame, 94% cavity.
Table FL-8
| Cavity Insulation Component | Framing Configuration4 (on-centre spacing) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 mm (12”) | 406 mm (16”) | 488 mm (19.2”) | 610 mm (24”) | ||
| Effective Thermal Resistance | |||||
| RSI | R | RSI | RSI | RSI | RSI |
| 5.46 | 31 | 5.03 | 5.09 | 5.15 | 5.21 |
| 5.64 | 32 | 5.17 | 5.23 | 5.30 | 5.36 |
| 5.81 | 33 | 5.30 | 5.37 | 5.43 | 5.51 |
| 5.99 | 34 | 5.43 | 5.50 | 5.58 | 5.66 |
| 6.16 | 35 | 5.56 | 5.63 | 5.72 | 5.80 |
| 6.34 | 36 | 5.69 | 5.77 | 5.86 | 5.95 |
| 6.52 | 37 | 5.81 | 5.91 | 6.00 | 6.10 |
| 6.69 | 38 | 5.94 | 6.03 | 6.13 | 6.24 |
| 6.87 | 39 | 6.06 | 6.17 | 6.27 | 6.38 |
| 7.04 | 40 | 6.18 | 6.29 | 6.40 | 6.52 |
| 7.22 | 41 | 6.30 | 6.42 | 6.54 | 6.67 |
| 7.40 | 42 | 6.42 | 6.55 | 6.68 | 6.81 |
| 7.57 | 43 | 6.54 | 6.67 | 6.80 | 6.94 |
| 7.75 | 44 | 6.66 | 6.80 | 6.94 | 7.09 |
| 7.93 | 45 | 6.78 | 6.92 | 7.07 | 7.23 |
| 8.10 | 46 | 6.89 | 7.04 | 7.20 | 7.36 |
| 8.28 | 47 | 7.00 | 7.16 | 7.33 | 7.50 |
| 8.45 | 48 | 7.11 | 7.28 | 7.45 | 7.63 |
| 8.63 | 49 | 7.23 | 7.40 | 7.58 | 7.77 |
| 8.81 | 50 | 7.34 | 7.52 | 7.71 | 7.90 |
| 8.98 | 51 | 7.44 | 7.63 | 7.83 | 8.03 |
| 9.16 | 52 | 7.55 | 7.75 | 7.95 | 8.17 |
| 9.33 | 53 | 7.66 | 7.86 | 8.07 | 8.29 |
NOTES:
- Applies to parallel chord trusses.
- Continuous surface air films that are eligible to be added: Exterior air film 0.03 m2K/W, and interior floor air film 0.16 m2K/W.
- Based on species groups Spruce-Pine-Fir and Hem-Fir. Other wood-based framing materials with a thermal resistance greater than 0.0085 (m2K/W) /mm, such as framing members containing or composed of OSB and plywood are also eligible.
- Equivalent Frame-Cavity Percentage – 304 mm (12”): 10.5% frame, 89.5% cavity; 406 mm (16”): 9% frame, 91% cavity; 488 mm (19.2”): 7.5% frame, 92.5% cavity; 610 mm (24”): 6% frame, 94% cavity.
5.2 Thermal Resistance of Continuous Materials
Continuous Materials
Table CM-1
| Description | Thermal resistance (RSI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Per mm (m2•°C/W/mm) |
As listed (m2•°C/W) | ||
| Air Films | |||
| Exterior: | ceiling, floors and walls wind 6.7 m/s (winter) | - | 0.03 |
| Interior: | ceiling (heat flow up) | - | 0.11 |
| floor (heat flow down) | - | 0.16 | |
| walls (heat flow horizontal) | - | 0.12 | |
| Vented Roof Air Space | |||
| Cathedral, flat and attic | - | 0.03 | |
| Air Cavities | |||
| Ceiling (heat flow up): | 13 - 20 mm air space | - | 0.15 |
| 21 - 90 mm air space | - | 0.16 | |
| Floors (heat flow down): | 13 - 19 mm air space | - | 0.16 |
| 20 – 39 mm air space | - | 0.18 | |
| 40 - 89 mm air space | - | 0.20 | |
| 90 mm air space | - | 0.22 | |
| Walls (heat flow horizontal): | 13 – 19 mm air space | - | 0.16 |
| 20 – 90 mm air space | - | 0.18 | |
| Cladding Materials | |||
| Brick: | fired clay (2400 kg/m2) | 0.0007 | - |
| concrete: sand and gravel, or stone (2400 kg/m2) | 0.0004 | - | |
| Siding: | Fibre-cement | 0.003 | - |
| Hardboard, 11 mm | - | 0.12 | |
| Plywood, 9.5 mm -lapped | - | 0.10 | |
| Vinyl, hollow-backed | - | 0.11 | |
| Vinyl, insulating-board-backed: 9.5 mm nominal | - | 0.32 | |
| Wood, 13 mm | - | 0.14 | |
| Stone: | Quartzitic and sandstone (2240 kg/m³) | 0.0003 | - |
| Calcitic, dolomitic, limestone, marble and granite (2240 kg/m³) | 0.0004 | - | |
| Stucco and mortar, cement/lime | 0.0009 | - | |
| Insulation Materials3 | |||
| Blanket and Batt: | |||
| Rock or glass fibre (CAN ULC S702) | R-12 (89/92 mm) | - | 2.11 |
| R-14 (89/92 mm) | - | 2.46 | |
| R-193 (R-20 batt compressed) (140 mm) | - | 3.34 | |
| R-20 (152 mm) | - | 3.52 | |
| R-22 (140/152 mm) | - | 3.87 | |
| R-22.5 (152 mm) | - | 3.96 | |
| R-24 (140/152 mm) | - | 4.23 | |
| Rock or glass fibre (CAN ULC S702), cont’d | R-28 (178/ 216 mm) | - | 4.93 |
| R-31 (241 mm) | - | 5.46 | |
| R-35 (267 mm) | - | 6.16 | |
| R-40 (279/300 mm) | - | 7.04 | |
| Boards and Slabs: | |||
| Polyisocyanurate (PIR) and Polyurethane (PUR) Board CAN/ULC S704) | Permeably faced | 0.03818 | - |
| Impermeably faced | 0.03937 | - | |
| Expanded Polystyrene Insulation Board (EPS) (CAN/ULC S701) | Type 1 | 0.026 | - |
| Type 2 | 0.028 | - | |
| Type 3 | 0.03 | - | |
| Extruded Polystyrene Insulation Board (XPS) (CAN/ULC S701) | Types 2, 3 & 4 | 0.035 | - |
| Rock fibre semi-rigid board | 0.0277 | - | |
| Glass fibre semi-rigid board | 0.0298 | - | |
| Spray-Applied: | |||
| Sprayed polyurethane foam, medium density closed cell (CAN/ULC S705.1) | 0.036 | - | |
| Sprayed polyurethane foam, light density open cell (CAN/ULC S705.1) | 0.026 | - | |
| Sprayed Cellulosic fibre (settled thickness) | 0.024 | - | |
| Spray-applied glass-fibre insulation: 16 kg/m³ (CAN/ULC S702) | 0.025 | - | |
| Spray-applied glass-fibre insulation: 28.8 kg/m³ (CAN/ULC S702) | 0.029 | - | |
| Loose-fill insulation: | |||
| Cellulose (CAN/ULC S703) | 0.025 | - | |
| Glass fibre loose fill insulation for attics - 112 mm to 565 mm (CAN/ULC S702) | 0.01875 | - | |
| Glass fibre loose fill insulation for walls (CAN/ULC S702) | 0.02865 | - | |
| Sheet Materials | |||
| Gypsum board | 0.0063 | - | |
| Insulating fibreboard (Type 2 sheathing) | 0.016 | - | |
| Plywood (generic softwood) | 0.0087 | - | |
| Plywood, Douglas-fir | 0.0111 | - | |
| Oriented strand board (OSB) | 0.0098 | - | |
| Structural Materials | |||
| Concrete | Sand and gravel or stone aggregate (2400 kg/m³) | 0.0004 | - |
NOTES:
- Values provided in the continuous materials layers table are in conformance with the proposed National Building Code of Canada (2012 revision). For simplification, some material categories (for example wood cladding) have been reduced to one row in this table where the NBC may have multiple rows for a material type. In such cases the lowest value from the NBC has been provided.
- Refer to Section 3.0 (Instructions) for how to determine the coding for items with an ‘xxx’ at the end
- Values are for generic insulation products. Where a specific insulation product is used in the assembly the thermal resistance value, or long term thermal resistance value, where applicable, of that product is permitted to be used as reported by the Canadian Construction Materials Centre (CCMC) in the evaluation of such a product.
- An RSI 3.52 (R20) per 152 mm batt compressed into a 140 mm cavity has a thermal resistance value of 3.34 (R19); if installed uncompressed in a 152 mm cavity (e.g., some manufactured framing products), it will retain its full thermal resistance value of 3.52 m2•K/W.
Appendix A: Examples
Example 1
| Element | Details | Table | Effective RSI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous materials | Roof sheathing1 | n/a | 0.00 |
| Continuous materials | Vented roof air space | CM-1 | 0.03 |
| Continuous materials | Blown in cellulose, 268 mm at 0.025 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 6.70 |
| Frame-Cavity | Roof truss bottom chord dimensional lumber: 38 mm x 89 mm (2"x4") spruce 610 mm (24") on-centre, R12 nominal cavity fill between bottom chords |
R1-1 | 1.76 |
| Continuous materials | Polyethylene vapour retarder2 | n/a | 0.00 |
| Continuous materials | Gypsum board, 12.7 mm at 0.0063 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 0.08 |
| Continuous materials | Air film interior, ceiling (heat flow up) | CM-1 | 0.11 |
| Total | 8.68 | ||
NOTES:
- Roof sheathing: is to the exterior of the vented roof air space, therefore excluded from calculation
- Polyethylene vapour retarder: negligible contribution to effective thermal resistance
Example 2
| Element | Details | Table | Effective RSI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous materials | Roof sheathing1 | n/a | 0.00 |
| Continuous materials | Vented roof air space2 | CM-1 | 0.03 |
| Frame-Cavity | Cathedral ceiling dimensional lumber: 38 mm x 235 mm (2"x10") spruce, 610 mm (24") on-centre, RSI 5.46 (R31) nominal cavity fill between roof joists |
R1-6 | 4.65 |
| Continuous materials | Polyethylene vapour retarder3 | n/a | 0.00 |
| Continuous materials | Air cavity, 19 mm air space, ceiling4 | CM-1 | 0.15 |
| Continuous materials | Gypsum board, 12.7 mm at 0.0063 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 0.08 |
| Continuous materials | Air film interior, ceiling (heat flow up) | CM-1 | 0.11 |
| Total | 5.02 | ||
NOTES:
- Roof sheathing: is to the exterior of the vented roof air space, therefore excluded from calculation
- Vented roof air space: created by 38 mm x 89 mm (2"x4") purlins on top of joists, cavity is completely filled with insulation
- Polyethylene vapour retarder: negligible contribution to effective thermal resistance
- Air cavity created by 19 mm (1”) furring on 406 mm (16”) centres
Example 3
| Element | Details | Table | Effective RSI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous materials | Roof sheathing1 | n/a | 0.00 |
| Continuous materials | Vented roof air space2, 3 | CM-1 | 0.03 |
| Frame-Cavity | Cathedral ceiling dimensional lumber: 38 mm x 235 mm (2"x10") spruce, 610 mm (24") on-centre, RSI 5.46 (R28) nominal cavity fill between roof joists3 |
R1-6 | 4.30 |
| Continuous materials | Polyethylene vapour retarder4 | n/a | 0.00 |
| Continuous materials | Air cavity, 19 mm air space, ceiling5 | CM-1 | 0.15 |
| Continuous materials | Gypsum board, 12.7 mm at 0.0063 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 0.08 |
| Continuous materials | Air film interior, ceiling (heat flow up) | CM-1 | 0.11 |
| Total | 4.67 | ||
NOTES:
- Roof sheathing: is to the exterior of the vented air space, therefore excluded from calculation
- Vented roof air space: created by leaving a 51 mm (2”) space between the plane of the top of the joist and the top of the insulation.
- The tables were developed on the assumption that the cavity insulation component is homogeneous and completely fills the frame cavity. There are some construction practices, such as in some cathedral ceilings, where the insulation does not completely fill the frame cavity in order to create a vented roof air space above the insulation. If no greater than a 50 mm roof air space is included above the insulation and between the framing members of a cathedral ceiling, the tables can be used in the normal manner, i.e., treat these assemblies as if the installed nominal insulation completely fills the cavity, and the vented air space is a continuous layer above the framing.
- Polyethylene vapour retarder: negligible contribution to effective thermal resistance
- Air space created by 19 mm (1”) furring on 406 mm (16”) centres.
Example 4
| Element | Details | Table | Effective RSI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous materials | Air film interior, floor (heat flow down) | CM-1 | 0.16 |
| Continuous materials | OSB subfloor, 19 mm at 0.0098 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 0.19 |
| Continuous materials | Polyethylene vapour retarder1 | n/a | 0.00 |
| Frame-Cavity | 63 mm x 302 mm (2.5"x11.875") engineered wood I joist: spruce/OSB, 488 mm (19.2") on-centre, RSI 5.46 (R31) nominal cavity fill between floor joists |
FL-7 | 5.03 |
| Continuous materials | Gypsum board, 12.7 mm at 0.0063 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 0.08 |
| Continuous materials | Air film exterior | CM-1 | 0.03 |
| Total | 5.49 | ||
NOTES:
- Polyethylene vapour retarder: negligible contribution to effective thermal resistance
Example 5
| Element | Details | Table | Effective RSI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous materials | Air film exterior | CM-1 | 0.03 |
| Continuous materials | Wood siding1 | n/a | 0.00 |
| Continuous materials | Vented air space created by furring for rain screen2 | n/a | 0.00 |
| Continuous materials | Extruded polystyrene (XPS), 38 mm at 0.035 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 1.33 |
| Continuous materials | OSB sheathing, 11mm at 0.0098 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 0.11 |
| Frame-Cavity | Stud dimensional lumber: 38 mm x 89 mm (2"x4") spruce, 406 mm (16") on-centre, RSI 1.49 (R12) nominal cavity fill between studs | WA-1 | 1.49 |
| Continuous materials | Polyethylene vapour retarder3 | n/a | 0.00 |
| Continuous materials | Gypsum board, 12.7 mm at 0.0063 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 0.08 |
| Continuous materials | Air film interior, wall (heat flow horizontal) | CM-1 | 0.12 |
| Total | 3.16 | ||
NOTES:
- Wood siding: is exterior of vented air space, therefore excluded from calculation
- Vented air space created by furring for rain screen: not a closed air space therefore excluded as an air cavity
- Polyethylene vapour retarder: negligible contribution to effective thermal resistance
Example 6
| Element | Details | Table | Effective RSI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous materials | Air film exterior | CM-1 | 0.03 |
| Continuous materials | Siding - vinyl, hollow-backed | CM-1 | 0.11 |
| Continuous materials | OSB sheathing, 11mm at 0.0098 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 0.11 |
| Frame-Cavity | Stud dimensional lumber: 38 mm x 140 mm (2"x6"), 406 mm (16") on-centre, RSI 4.23 (R24) nominal cavity fill between studs |
2.66 | |
| Continuous materials | Polyethylene vapour retarder1 | n/a | 0.00 |
| Continuous materials | Gypsum board, 12.7 mm at 0.0063 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 0.08 |
| Continuous materials | Air film interior, wall (heat flow horizontal) | CM-1 | 0.12 |
| Total | 3.11 | ||
NOTES:
- Polyethylene vapour retarder: negligible contribution to effective thermal resistance
Example 7
| Element | Details | Table | Effective RSI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous materials | Air film exterior | CM-1 | 0.03 |
| Continuous materials | Siding - vinyl, hollow-backed | CM-1 | 0.11 |
| Continuous materials | Extruded polystyrene (XPS), 25 mm at RSI 0.035/mm | CM-1 | 0.88 |
| Continuous materials | OSB sheathing, 11mm at 0.0098 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 0.11 |
| Frame-Cavity | Stud dimensional lumber: 38 mm x 140 mm (2"x6"), 406 mm (16") on-centre, RSI 3.87 (R22) nominal cavity fill between studs |
2.55 | |
| Continuous materials | Polyethylene vapour retarder1 | n/a | 0.00 |
| Continuous materials | Gypsum board, 12.7 mm at 0.0063 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 0.08 |
| Continuous materials | Air film interior, wall (heat flow horizontal) | CM-1 | 0.12 |
| Total | 3.88 | ||
NOTES:
- Polyethylene vapour retarder: negligible contribution to effective thermal resistance
Example 8
| Element | Details | Table | Effective RSI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous materials | Air film exterior | CM-1 | 0.03 |
| Continuous materials | Siding - vinyl, hollow-backed | CM-1 | 0.11 |
| Continuous materials | OSB sheathing, 11mm at 0.0098 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 0.11 |
| Frame-Cavity | Type 2 EPS, 140 mm Insulation Core, RSI 3.92 (R22) | WA-3 | 2.94 |
| Continuous materials | OSB sheathing, 11mm at 0.0098 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 0.11 |
| Continuous materials | Gypsum board, 12.7 mm at 0.0063 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 0.08 |
| Continuous materials | Air film interior, wall (heat flow horizontal) | CM-1 | 0.12 |
| Total | 3.50 | ||
Example 9
| Element | Details | Table | Effective RSI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous materials | Air film exterior | CM-1 | 0.03 |
| Continuous materials | Siding - vinyl, hollow-backed | CM-1 | 0.11 |
| Continuous materials | Expanded polystyrene (Type 2 EPS), 63 mm at 0.028 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 1.76 |
| Continuous materials | Concrete wall - 200 mm at 0.0004 RSI/mm1 | CM-1 | 0.08 |
| Continuous materials | Type 2 EPS, 63 mm at 0.028 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 1.76 |
| Continuous materials | Gypsum board, 12.7 mm at 0.0063 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 0.08 |
| Continuous materials | Air film interior, wall (heat flow horizontal) | CM-1 | 0.12 |
| Total | 3.94 | ||
NOTES:
- Concrete wall: thermal bridging effect of plastic web-spacer can be ignored
Example 10
| Element | Details | Table | Effective RSI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous materials | Concrete foundation wall, 200 mm at 0.0004 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 0.08 |
| Continuous materials | Extruded polystyrene (XPS), 25 mm at 0.035 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 0.87 |
| Frame-Cavity | Stud dimensional lumber: 38 mm x 140 mm (2"x6") spruce with RSI=1.19 m2K/W, 610 mm (24") on-centre, RSI 3.52 (R20) nominal cavity fill between studs |
WB-2 | 2.81 |
| Continuous materials | Gypsum board, 12.7 mm at 0.0063 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 0.08 |
| Continuous materials | Air film interior, wall (heat flow horizontal) | CM-1 | 0.12 |
| Total | 3.96 | ||
Example 11
| Element | Details | Table | Effective RSI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous materials | Air film interior, floor (heat flow down) | CM-1 | 0.16 |
| Continuous materials | Concrete floor slab, 100 mm at 0.0004 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 0.04 |
| Continuous materials | Extruded polystyrene (XPS), 51 mm 0.035 RSI/mm | CM-1 | 1.79 |
| Total | 1.99 | ||
Page details
- Date modified: